My CSA Work Blog
Collectibles
- Reusable data structures for storing, retrieving, and manipulating groups of objects.
- Examples:
ArrayList,HashSet,HashMap.
Why Use Collectibles?
- Efficiently manage groups of objects.
- Built-in methods for searching, sorting, and filtering.
- Improve code readability and maintainability.
Types of Collectibles
- List: Ordered, allows duplicates (e.g.,
ArrayList,LinkedList). - Set: Unordered, no duplicates (e.g.,
HashSet,TreeSet). - Map: Key-value pairs (e.g.,
HashMap,TreeMap). - Queue: FIFO (e.g.,
LinkedList,PriorityQueue). - Stack: LIFO (e.g.,
Stack,ArrayDeque). - Deque: Double-ended queue (e.g.,
ArrayDeque,LinkedList).
Benefits
- Simplify data management.
- Reduce boilerplate code.
- Improve performance for common operations.
Calculator Enactment
Queue Tasks
- Modify the
CalculatorQueueto support more complex operations, such as multiplication and division. - Add a method to handle invalid operations and display an error message.
- Create a method to display all operations before processing them and track the result after each operation.
Stack Tasks
- Modify the
CalculatorStackto reverse the order of addition and handle operations in the LIFO sequence. - Add a method to handle invalid operations and display an error message.
- Create a method to display all operations before processing them and track the result after each operation.
How to Use
- Use the Queue for processing operations in the order they are added (FIFO).
- Use the Stack for processing operations in reverse order (LIFO).
- Both structures can be enhanced to handle advanced tasks like parentheses or postfix evaluation.
Merge Sorting
How It Works
- Merge sort is a divide and conquer algorithm that repeatedly divides the array into smaller subarrays, sorts them, and merges them back together.
- Steps:
- Divide the array into two halves.
- Sort each half recursively.
- Merge the two halves back together.
- Repeat until the entire array is sorted.
Key Features
- Time Complexity:
- Best, Worst, and Average Case: O(n log n).
- Efficient for large datasets due to its logarithmic growth.
- Stability:
- Merge sort is stable, meaning it preserves the order of elements with equal values.
- Comparison with Other Algorithms:
- Faster than bubble sort for large arrays.
- Similar time complexity to quicksort but preferred for stability and larger datasets.
Pros
- Highly efficient for large and small arrays.
- Stable sorting algorithm.
- Handles large datasets well due to its predictable time complexity.
Cons
- Requires additional memory for temporary arrays during the merge process.
- Slower than simpler algorithms like bubble sort for small datasets.
Example Task
- Write a Java program to merge two already sorted arrays into one sorted array.
- Bonus: Modify the program to count the number of comparisons made during sorting.
JQuery
How It Works
- JQuery is a lightweight JavaScript library that simplifies HTML document traversal, event handling, and animations.
- It uses selectors to target HTML elements and apply actions or effects.
Key Features
- Selectors: Use
$()to select HTML elements. For example:$("button"): Selects all<button>elements.$("p"): Selects all<p>elements.
- Event Handling: Attach events like
click,hover, etc., to elements.- Example:
$("button").click(function() { ... })triggers an action when a button is clicked.
- Example:
- Effects: Provides methods like
hide(),show(),fadeIn(), andfadeOut()to manipulate element visibility.
Example Code
$(document).ready(function() { // Ensures the DOM is fully loaded
$("button").click(function() { // Selector for all buttons
$("p").hide(); // Hides all <p> elements when a button is clicked
});
});
Final Thoughts
This class has been an incredible journey! I’ve learned so much—from mastering data structures and algorithms to building interactive web pages with JQuery. Each project has taught me how to think critically and solve problems efficiently, preparing me for future challenges in computer science.
FRQ Work
I also worked on the College Board FRQ and finished multiple parts seen here:
public static int arraySum(int[] arr) {
int result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
result += arr[i];
}
return result;
}
public static int[] array2DSum(int[][] arr2d) {
int[] sum = new int[arr2d.length];
for(int r = 0; r < arr2d.length; r++) {
sum[r] += arraySum(arr2d[r]);
}
return sum;
}
public static boolean isDiverse(int[][] arr2d) {
int[] sumRow = array2DSum(arr2d);
for(int i = 0; i < sumRow.length; i++) {
for(int j = i + 1; j < sumRow.length; j++) {
if(sumRow[i] == sumRow[j]) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
int[][] arr2d = {
{1, 3, 3, 7, 3},
{10, 10, 4, 6, 2},
{5, 3, 5, 9, 6},
{7, 6, 4, 2, 1}
};
System.out.println(arraySum(array));
int[] result = array2DSum(arr2d);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result));
System.out.println(isDiverse(arr2d));
College Board MCQ Work

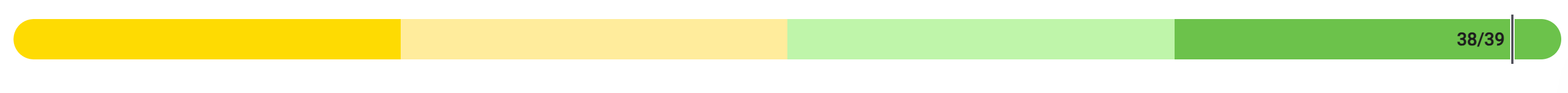
Things I Struggled On:
- 2D Arrays: I found it challenging to understand how to manipulate and access elements in 2D arrays.
- JQuery: I struggled with understanding how to use JQuery selectors and event handling effectively.
- Merge Sort: I had difficulty grasping the concept of dividing and merging arrays in merge sort.
How I Will Improve:
- 2D Arrays: I will practice more problems involving 2D arrays and seek help from classmates or online resources.
- JQuery: I will watch tutorials and practice using JQuery selectors and event handling in small projects.
- Merge Sort: I will review the merge sort algorithm and implement it in different scenarios to solidify my understanding.
Study Plan
I will be studying for the AP exam by reviewing the following topics:
- Data Structures: Arrays, Lists, Sets, Maps.
- Algorithms: Sorting (merge sort), searching, recursion.
- Web Development: HTML, CSS, JavaScript, JQuery.
- AP Exam Format: Multiple-choice questions, free-response questions.
I will also practice the 2D Arrays because its something that I always struggle with. I will use the following resources:
- AP Classroom: Practice multiple-choice and free-response questions.
- Online Tutorials: Websites like Khan Academy and Codecademy for additional practice.
- Study Groups: Collaborate with classmates to discuss concepts and solve problems.
I will try to plan and stay organized by creating a study schedule and setting specific goals for each study session. I will also take breaks to avoid burnout and stay motivated as well as making burndown lists to keep track of my progress.